

Link to the specific question (not just the name of the question) that contains the content and a description of Sufficient detail to permit Varsity Tutors to find and positively identify that content for example we require

Please follow these steps to file a notice:Ī physical or electronic signature of the copyright owner or a person authorized to act on their behalf Īn identification of the copyright claimed to have been infringed Ī description of the nature and exact location of the content that you claim to infringe your copyright, in \ On or linked-to by the Website infringes your copyright, you should consider first contacting an attorney. Thus, if you are not sure content located
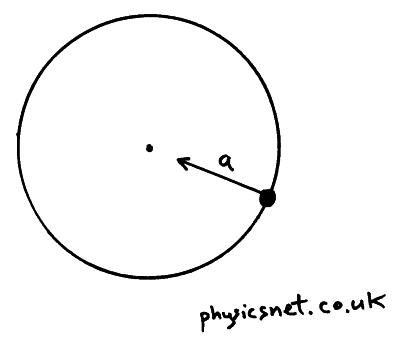
Misrepresent that a product or activity is infringing your copyrights. Please be advised that you will be liable for damages (including costs and attorneys’ fees) if you materially Your Infringement Notice may be forwarded to the party that made the content available or to third parties such Means of the most recent email address, if any, provided by such party to Varsity Tutors. Infringement Notice, it will make a good faith attempt to contact the party that made such content available by If Varsity Tutors takes action in response to Information described below to the designated agent listed below. Or more of your copyrights, please notify us by providing a written notice (“Infringement Notice”) containing If you believe that content available by means of the Website (as defined in our Terms of Service) infringes one For example, when the ball is at the bottom of the circle, the force of gravity is away from the center of the circle, so tension must be higher to keep the center pull constant. The force of gravity is always down and constant, so the tension needs to change in order to keep the center pulling force the same. There are two forces on the ball, gravity and tension. For example, at the top of its path, the centripetal force must be down because that's the direction of the center of its circle of motion, but at the bottom, the centripetal force must be up. This is true because the ball needs the same center pulling force (centripetal force) throughout its path, but this centripetal force is constantly changing direction. The only the changing is the tension in the string. The ball's angular momentum is always constant since its mass, the radius of the circle it's traveling in, and its speed are constant. The string's pull on the ball is always perpendicular to the ball's motion, so it isn't doing any work, and thus has a constant rate of work. The force of gravity on the ball is always its mass times gravity, which is constant.

Let's go through each answer choice one by one. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License. We recommend using aĪuthors: Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs Use the information below to generate a citation. Then you must include on every digital page view the following attribution: If you are redistributing all or part of this book in a digital format, Then you must include on every physical page the following attribution: If you are redistributing all or part of this book in a print format, Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the (a) Calculate the acceleration due to gravity at Neptune due to Pluto when they are 4. To illustrate that Pluto has a minor effect on the orbit of Neptune compared with the closest planet to Neptune: But it now appears that the discovery was fortuitous, because Pluto is small and the irregularities in Neptune’s orbit were not well known. Pluto was subsequently discovered near its predicted position. The existence of the dwarf planet Pluto was proposed based on irregularities in Neptune’s orbit.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
